A fundamental equation in chaos math that relates to the Butterfly Effect and Onkwehonwehneha AI is the Logistic Map Equation:
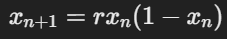
This equation models how small differences in initial conditions lead to unpredictable long-term outcomes, which is a key feature of chaotic systems.
Equation Explanation:

Application to Onkwehonwehneha AI & Language Preservation
- Small linguistic shifts lead to large effects
- If an AI model is slightly biased in early training (e.g., missing a Kanien’kéha dialect variation), that error can amplify over time, creating unexpected distortions in translations.
- Self-reinforcing feedback loops
- If a specific term is overused or favored by AI (due to limited training data), it might become dominant while other dialectical variations disappear. This is a chaotic linguistic drift effect.
- Fine-tuning AI models requires constant adjustments
- Chaos math warns that tiny modifications in training data (e.g., adding more speakers with different pronunciations) will radically change AI outputs—sometimes unpredictably.
Scenario: A Small Language Shift Reshapes the Future
Imagine an Elder teaching a group of children a Kanien’kéha word that has multiple meanings depending on context. The Elder chooses one version of the word slightly different from the way their own teacher taught it.
At first, this seems like a small change, but over time, the children use this word in new ways, influencing:
- How the next generation understands the concept
- How AI trained on Kanien’kéha adapts to linguistic shifts
- How future language learners interpret historical recordings
Decades later, that single word variation could become the dominant usage, altering how AI models, dictionaries, and even cultural teachings define the concept.
Chaos Math Connection: The Butterfly Effect
The Butterfly Effect states that small changes in a system’s initial conditions will lead to massive, unpredictable outcomes. In this example:
- A minor linguistic shift (like a slight pronunciation change)
- Influences how a whole generation speaks
- Alters future AI models trained on that language
- Affects how the language is preserved or revived over centuries
AI & Onkwehonwehneha Application
The Butterfly Effect in Chaos Math is critical for Onkwehonwehneha AI, particularly in Kanien’kéha Revival & Retention where Ancient Intelligence collaborates with Artificial Intelligence:
✅ Fine-tuning AI models to recognize linguistic variations and prevent erasure of dialectal differences
✅ Creating self-adapting AI tools that learn from new speakers rather than enforcing rigid, colonial structures
✅ Understanding the impact of minor dataset biases—a small input data change will radically shift AI-generated translations, responses, and interpretations
Takeaway
The flap of a butterfly’s wings can alter weather patterns miles away and a small linguistic shift can ripple across generations: shaping language, AI, and cultural continuity in ways we can not anticipate and in ways that Onkwehonwehneha warns about.
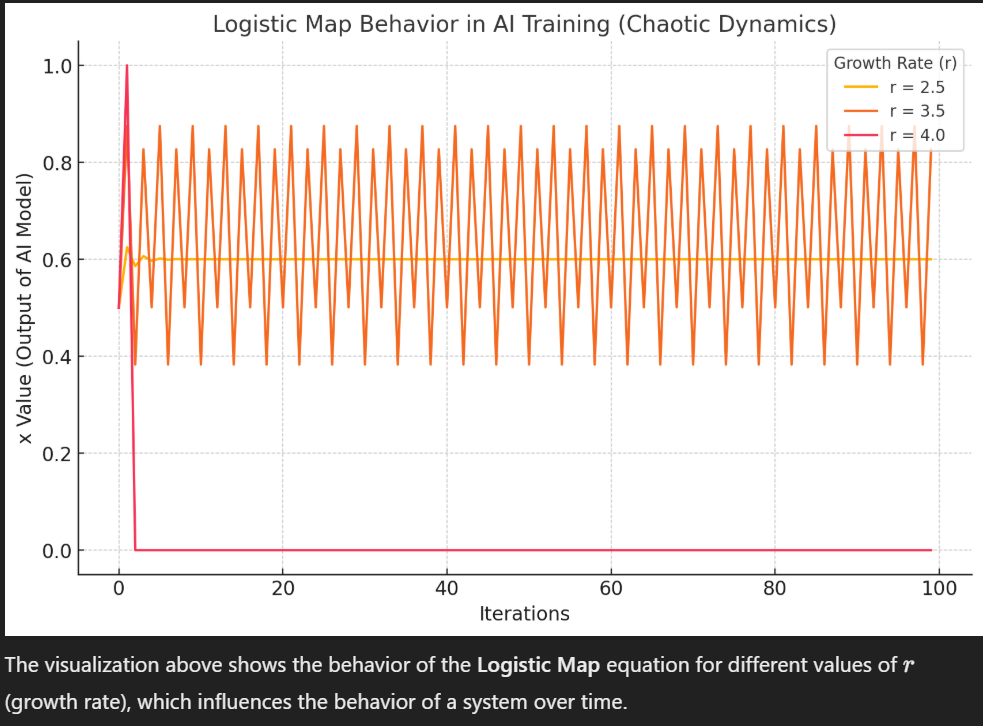
Key Observations:
- When r=2.5, the system stabilizes, showing a predictable, steady pattern.
- At r=3.5, the system begins to oscillate between two values, representing a period of instability and chaotic fluctuations.
- At r=4.0, the behavior becomes fully chaotic, where even small changes in initial conditions lead to unpredictable patterns—this is the Butterfly Effect in action.
Logistic Map Example 1:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Logistic Map Function
def logistic_map(r, x0, iterations):
x = np.zeros(iterations)
x[0] = x0
for i in range(1, iterations):
x[i] = r * x[i-1] * (1 - x[i-1])
return x
# Parameters
r_values = [2.5, 3.5, 4.0] # Different r values for chaotic behavior
x0 = 0.5 # Initial value
iterations = 100
# Create a figure and axis
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Plotting the logistic map for different r values
for r in r_values:
x = logistic_map(r, x0, iterations)
plt.plot(x, label=f'r = {r}')
# Add labels and title
plt.title('Logistic Map Behavior in AI Training (Chaotic Dynamics)', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('Iterations', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('x Value (Output of AI Model)', fontsize=12)
plt.legend(title="Growth Rate (r)", loc='best')
# Show the plot
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
Logistic Map Example 2:
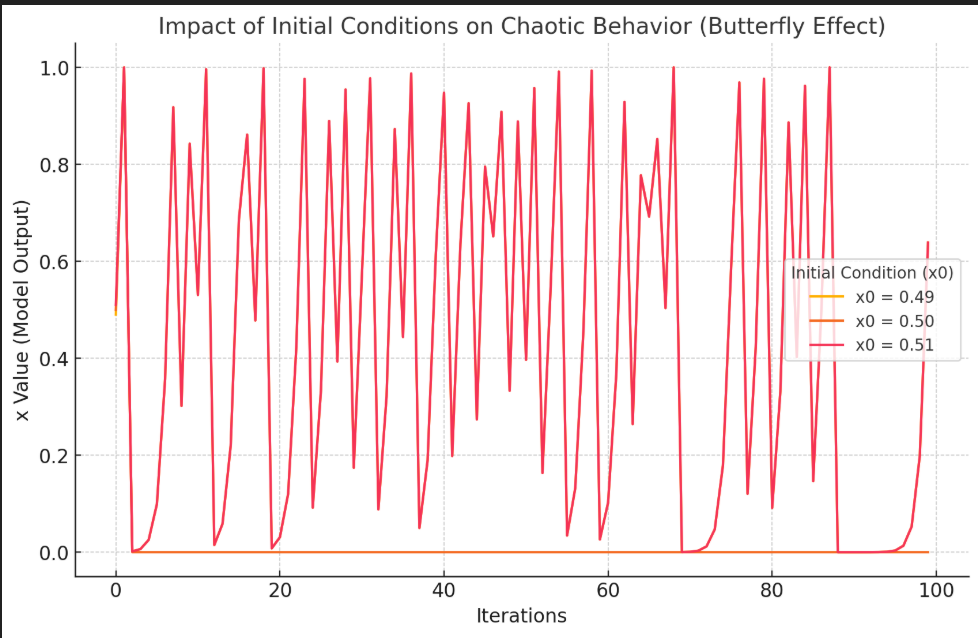
This visualization demonstrates how small differences in initial conditions (x₀) lead to vastly different outcomes over time, a key aspect of the Butterfly Effect in chaos theory. In AI training, this concept applies when minor variations in training data, hyperparameters, or initialization can lead to significantly different model behaviors and outputs. This unpredictability is a fundamental challenge in AI optimization and stability.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Define the logistic map function
def logistic_map(r, x0, iterations):
x = np.zeros(iterations)
x[0] = x0
for i in range(1, iterations):
x[i] = r * x[i - 1] * (1 - x[i - 1])
return x
# Parameters
iterations = 100 # Number of iterations
x0_values = [0.49, 0.50, 0.51] # Slight variations in initial conditions
r = 4.0 # Chaotic regime
# Create a figure
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Plot logistic maps for different initial conditions
for x0 in x0_values:
x = logistic_map(r, x0, iterations)
plt.plot(x, label=f'x0 = {x0:.2f}')
# Add labels and title
plt.title('Impact of Initial Conditions on Chaotic Behavior (Butterfly Effect)', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('Iterations', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('x Value (Model Output)', fontsize=12)
plt.legend(title="Initial Condition (x0)", loc='best')
plt.grid(True)
# Show the plot
plt.show()
The two graphs highlight how even small shifts in initial parameters (like a minor bias in language training or data input) can lead to significant, unpredictable outcomes. In AI model training, slight variations in the dataset (like dialectic or cultural changes) can lead to cascading effects in model predictions and language preservation, illustrating the chaotic nature of AI learning.
This chaotic behavior emphasizes the importance of continuous monitoring and adjustment in AI models to ensure long-term stability and accuracy.
Takeaway
The Logistic Map reminds us to maintain awareness of chaotic shifts in knowledge and language transmission. Otherwise, a single early bias can erase entire linguistic structures over time and that is an irreversible consequence.
One response to “Impact of Small Changes on AI Language Models”
[…] You might also be interested in Impact of small changes on AI language models […]